Robots have always been known for their rigid bodies, devoid of the pliability and flexibility that humans possess. However, a new field known as “soft robotics” aims to change that by incorporating the characteristics of living organisms into robot designs. Until now, though, soft robotics hasn’t fully taken off due to the difficulty of mass-producing and integrating softer components. Fortunately, researchers at the University of Virginia have developed a groundbreaking manufacturing process for weaving soft materials such as fabrics, rubbers, and gels. This breakthrough has the potential to spark a revolution in the field of soft robotics.
A Weaving Innovation
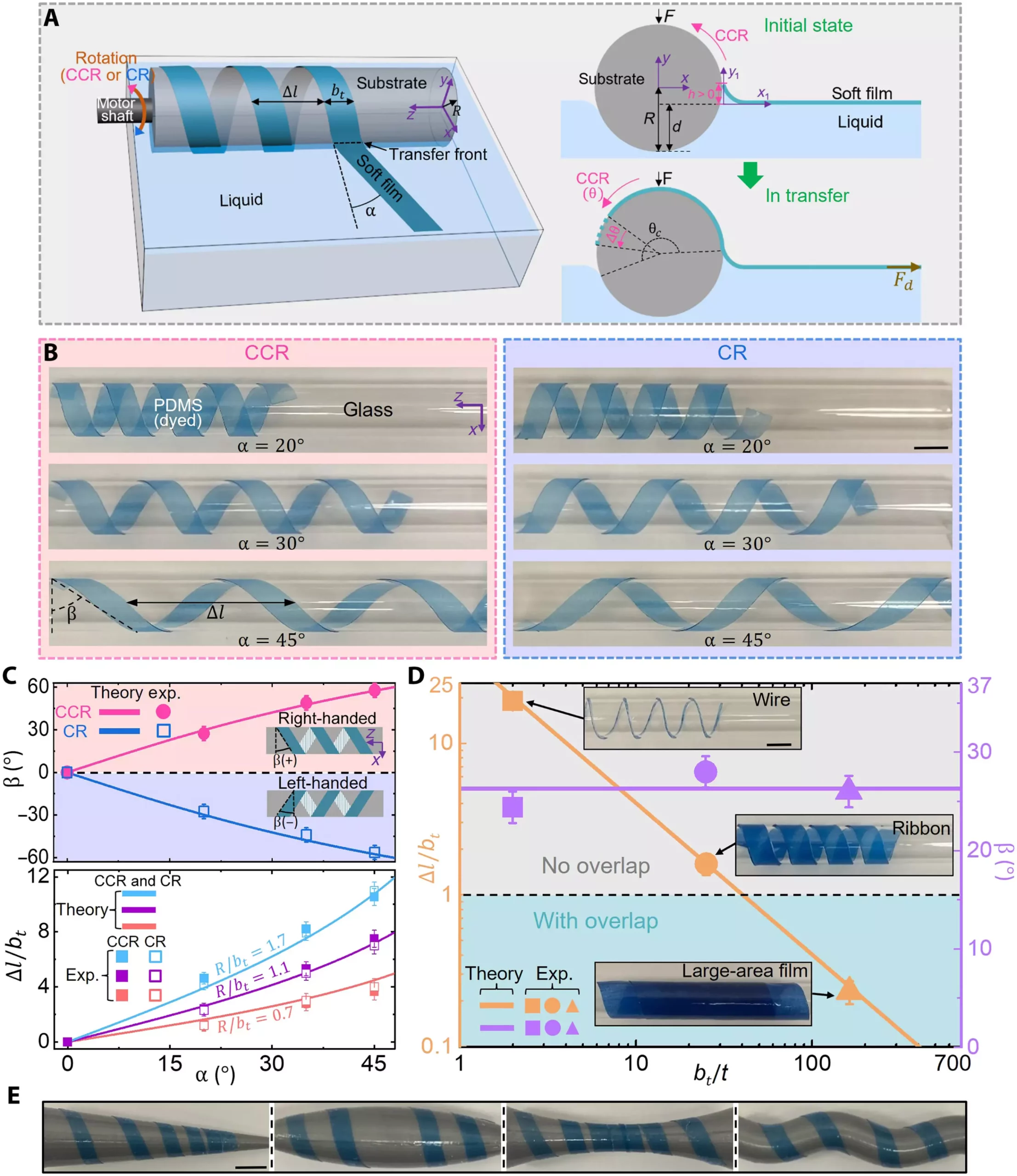
The team of researchers at the University of Virginia recently introduced a patent-pending design in an article published in Science Advances. Led by Associate Professor Baoxing Xu, the team has successfully created a manufacturing process that enables soft materials to be woven into intricate 3D spatial structures. This novel approach is a significant advancement from existing industry methods that are primarily designed for rigid materials or nanoparticles, lacking the ability to handle soft continuous structures like films, ribbons, and wires.
The Liquid-based Rolling Transfer System
Central to this innovative process is a liquid-based rolling transfer system. Unlike conventional methods, this system allows for precise adjustments during the weaving process, enabling fast and damage-free manufacturing. By harnessing the capabilities of this system, soft materials can now be seamlessly integrated into the designs of various gadgets, opening up a world of possibilities for soft robotics.
While the implications for soft robotics are immense, the applications of this manufacturing process extend far beyond just that field. The newfound ability to weave soft materials into complex outer surfaces holds the potential to revolutionize wearable electronics, biomedical devices, and a myriad of internet-based products. With this breakthrough, researchers and engineers can now explore novel designs and functionalities that were previously unattainable, pushing the boundaries of technological innovation.
The successful development of a manufacturing process for weaving soft materials marks a crucial step towards a soft robotics revolution. With this breakthrough, the barrier to mass production and integration of softer components has been shattered, paving the way for the creation of more lifelike and versatile robotic systems. The incorporation of soft materials into robotics holds the promise of safer, more adaptable machines that can interact with humans and their environment in a more natural and seamless manner.
The Future Looks Soft and Exciting
As the field of soft robotics continues to evolve, the newfound ability to weave soft materials will fuel its rapid progression. Research and development efforts will now be empowered to explore new design possibilities and push the boundaries of what robots can achieve. From enhancing prosthetic limbs to creating advanced exoskeletons, the applications of soft robotics are limitless. Ultimately, this innovative manufacturing process brings us one step closer to a future where robots possess the pliability and versatility of living organisms, forever transforming the way we interact with and benefit from these machines.

Leave a Reply